Our Sun is a star, but it is closer to us
than any other star. Like all stars, it
is a massive ball of burning gas, fed
by constant explosions. Without it,
our planet would be lifeless.
The Sun
Solar wind
The Sun sends out a stream of invisible particles,
called the solar wind. When these pass Earth’s North
and South Poles, they can create stunning colours.
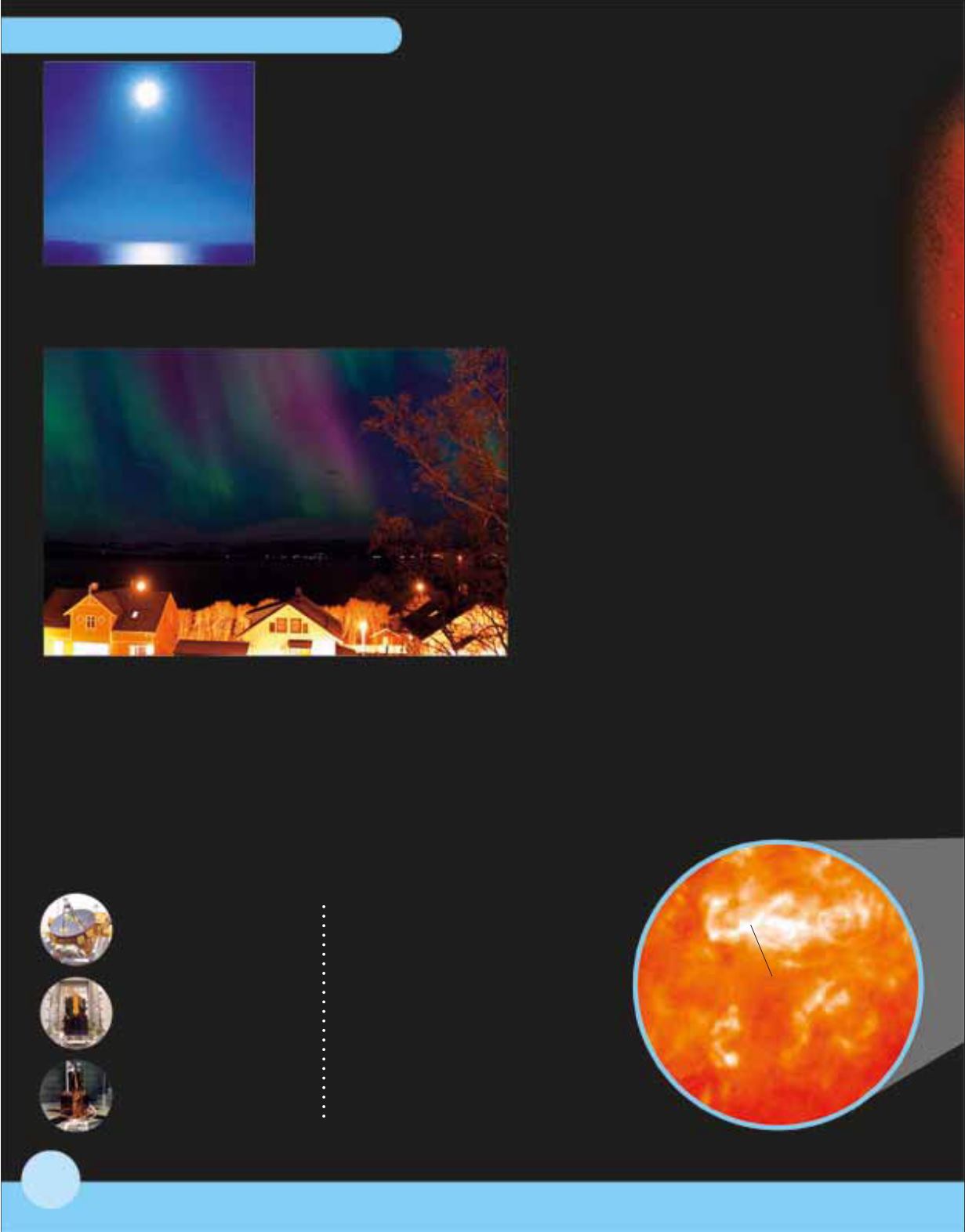
A hot spot?
White areas show places
where the Sun’s surface
temperature is higher
than elsewhere. Cooler,
dark areas, called
sunspots, sometimes
appear on the surface.
Does the Sun spin?
288
The universe
The Sun is white. Its colour is best
seen when reflected in water. Never
look directly at the Sun.
These hotspots
are called
faculae.
Investigating the Sun
Various space probes have been
designed to study the Sun.
SOHO
was launched in
1995 to observe the Sun
and solar activity.
TRACE
was launched in
1998 to study the Sun’s
atmosphere.
Ulysses
was launched in
1990 to look at the Sun’s
polar regions.
Long lived
The Sun was born just
under five billion years
ago. Although it burns four
million tonnes (tons) of fuel
each second, it is so big that
it will continue to burn for
another five billion years.
Shimmering lights
can light up the
skies towards
the Earth’s polar
regions.


